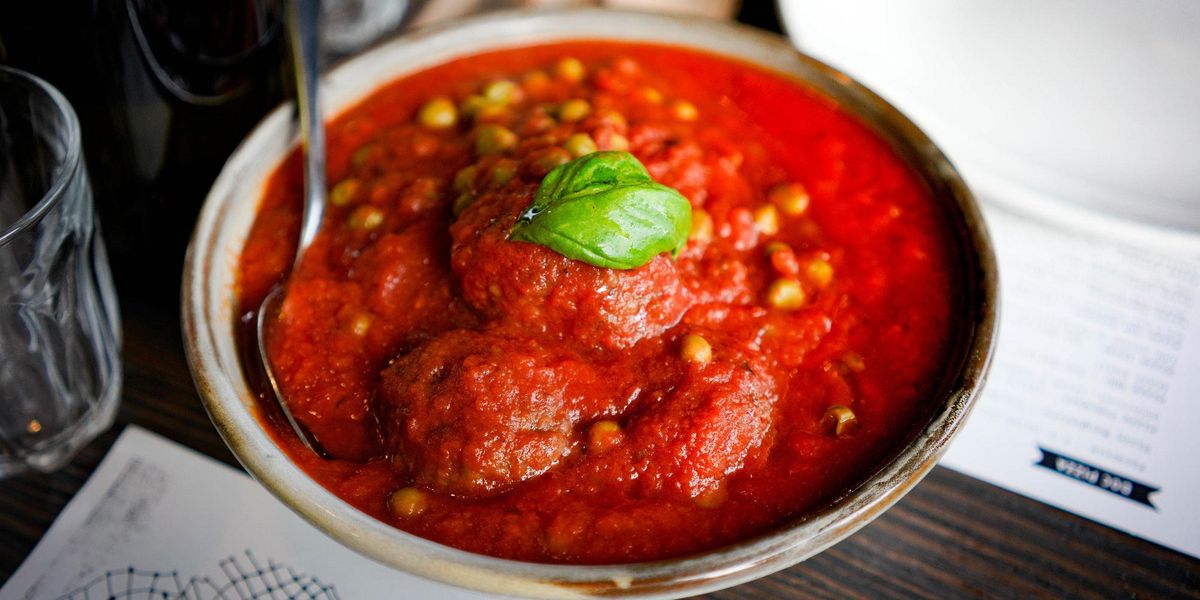
Four popular organic pasta sauces have detectable levels of fluorine, an indicator of toxic PFAS, according to a new report from Mamavation.
Partnering with EHN.org, the environmental wellness blog and community Mamavation tested 55 sauces and found levels of fluorine ranging from 10 parts per million (ppm) up to 21 ppm in four of the sauces: 365 Whole Foods Organic Tomato Basil Pasta Sauce, Muir Glen Organic Italian Herb Pasta Sauce, Organicville Italian Herb Pasta Sauce, and Trader Joe’s Organic Tomato Basil Marinara.
EHN.org partially funded the testing and Pete Myers, chief scientist of Environmental Health Sciences, which publishes Environmental Health News, reviewed the findings.
Related: Investigation: PFAS on our shelves and in our bodies
While the testing doesn’t prove per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are in the sauces, fluorine is a strong indicator of the “forever chemicals”— which have been linked to everything from cancer to birth defects to lower vaccine effectiveness.
PFAS in our food
The new investigation is the latest from Mamavation, which previously found fluorine in everyday products such as yoga pants and leggings and clean beauty brands’ makeup.
PFAS has been found in food before: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2019 reported PFAS in several types of food, including meats, seafood, and grocery store chocolate cake.
Related: What are PFAS?
However, Mamavation found evidence of the chemicals in brands that are marketed as organic. It’s unclear how PFAS make it into certain foods, but due to widespread use of PFAS across industries, the chemicals can contaminate consumer goods though manufacturing lubricants and coatings, misidentified raw materials, pesticides, personal protective equipment, and plastic packaging.
Ongoing PFAS testing
While the testing is concerning, 92% of sauces tested had no detectable fluorine.
“The good news is that only 8% of the tomato and pasta sauces contained PFAS. But why should there be any in our food?” Linda Birnbaum, who served as the Director of the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) and National Toxicology Program for more than a decade and who also reviewed the investigation, told Mamavation.
The testing is part of an ongoing effort by Mamavation and EHN.org to identify PFAS in common consumer products. See the full results at Mamavation.
Follow our PFAS testing project with Mamavation at the series landing page.
Want to know more about PFAS? Check out our comprehensive guide.
Have something you want tested for PFAS? Let us know and write us at feedback@ehn.org.
Banner photo credit: Fidel Fernando/Unsplash