The U.S. is among the countries that allow for the highest levels of cell tower radio-frequency (RF) radiation in the environment. Many countries are far ahead of the United States, adopting stronger protections for children by limiting cell tower radiation exposure, banning cell towers at schools, and requiring consumer warnings on cell phones, while the U.S. continues to rely on an outdated regulatory framework that fails to prioritize child health.
The U.S. Permits High Cell Tower Radiation Exposure
Cell towers and 5G emit RF radiation
Cell towers, including 4G and 5G cellular antennas, emit radio frequency (RF) radiation, a type of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation. Many scientists recommend caution because studies have reported a range of harmful health impacts after prolonged exposure.
This graph shows the selected countries’ regulations regarding public exposure limits for 1800 MHz W/m2 equivalent plane wave density RF radiation, applicable to schools and/or homes. Many countries have limits that apply to places of “sensitive use” such as apartment buildings, schools, hospitals, permanent workplaces, and children’s playgrounds. The U.S. has no specific safeguards for children.
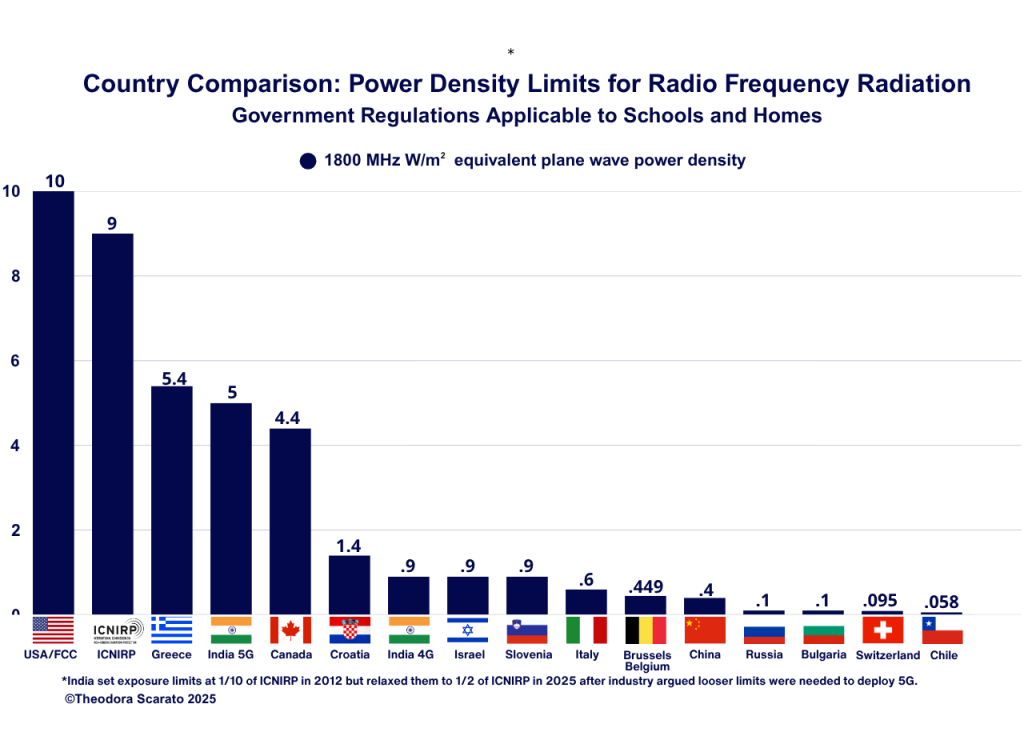
- References: Worldwide Limits for Cell Tower Radiation
The U.S. is among the countries that allow for the highest levels of cell tower radiofrequency (RF) radiation in the environment. This graph shows the selected countries’ regulations regarding public exposure limits for 1800 MHz W/m2 equivalent plane wave density RF radiation, applicable to schools and/or homes. The U.S. has no specific safeguards for children.
This is from the published paper in Frontiers in Public Health entitled “U.S. policy on wireless technologies and public health protection: regulatory gaps and proposed reforms.”
Country: United States of America
Authority: US Federal Communications Commission
Exposure Limit on Graph: 10 W/m2 for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Unlike other countries, the US does not have any limits applicable to sensitive areas such as schools, daycares, or residential areas. US limits were set in 1996 and have not changed since that date.
Source: U.S. FCC Limits for Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE): 47 CFR 1.1310, Radiofrequency radiation exposure limits. National Archives (2025).
See also: International Commission on the Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields (ICBE-EMF), (2022). Scientific evidence invalidates health assumptions underlying the FCC and ICNIRP exposure limit determinations for radiofrequency radiation: implications for 5G. Environ Health. Oct 18;21(1):92.
ICNIRP
ICNIRP is an invite-only private group of under 13 people accountable to no one. ICNIRP has been widely criticized for longstanding conflicts of interest, as many of its members over the years have professional ties to the telecommunications industry. Independent scientists, including those of the International Commission on the Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields (ICBE-EMF), have documented that these conflicts contribute to ICNIRP’s persistent dismissal of non-thermal biological effects and its reliance on outdated 1980s-era research, resulting in exposure limits food wireless and non-ionizing EMF that do not reflect the scientific evidence on cell tower, cell phone and EMF risk.
ICNIRP Exposure Limit on Graph: 9 W/m2 for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). (2020).
Guidelines for limiting exposure to electromagnetic fields (100 kHz to 300 GHz).
Health Physics, 118(5), 483–524.
Scientific References on ICNIRPs Conflicts of Interest
Vanheste T, Lambert E. The International Commission on Non-Ionizing 2783 Radiation Protection: Conflicts of Interest, Corporate Capture and the Push for 5G. (2020). Available online at: https://klaus- buchner.eu/wp- content/uploads/2020/06/ 2786 ICNIRP- report- FINAL- JUNE- 2020- 2.pdf
Lin JC (2025) Health and safety practices and policies concerning human exposure to RF/microwave radiation. Front. Public Health 13:1619781. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2025.1619781
Nordhagen, Else K. and Flydal, Einar. (2022). Self-referencing authorships behind the ICNIRP 2020 radiation protection guidelines. Reviews on Environmental Health.
Ben Ishai, P., Davis, D., Taylor, H., & Birnbaum, L. (2022). Problems in evaluating the health impacts of radio frequency radiation. Environmental research, 115038. Advance online publication.
International Commission on the Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Fields (ICBE-EMF), (2022). Scientific evidence invalidates health assumptions underlying the FCC and ICNIRP exposure limit determinations for radiofrequency radiation: implications for 5G. Environ Health. Oct 18;21(1):92.
Hardell, L., Nilsson, M., Koppel, T., & Carlberg, M. (2021). Aspects on the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) 2020 Guidelines on Radiofrequency Radiation. Journal of Cancer Science and Clinical Therapeutics, 5(2), 250–285.
Pascual GD. Not Entirely Reliable: Private Scientific Organizations and Risk Regulation – The Case of Electromagnetic Fields. European Journal of Risk Regulation. 2013;4(1):29-42. doi:10.1017/S1867299X00002774
Weller S, McCredden JE. Understanding the public voices and researchers speaking into the 5G narrative. Front Public Health. 2024 Jan 12;11:1339513. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/public-health/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1339513/full
Greece
Authority: Hellenic Atomic Energy Commission (EEAE)
Exposure Limit on Graph: for 5.4 W/m2 for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Greece has two sets of restrictions, one of which is specifically aimed at areas where children are cared for or schools. The exposure limit presented here is for cellular antennas closer than 300 m to sensitive locations (schools, kindergartens, hospitals, care homes): 2.7 W/m2 at 900 MHz and 5.4 W/m2 at 1800 MHz; 6 W/m2 at 2100 MHz. For areas further than 300 m, the limit is 3.1 W/m2 at 900 MHz; 6.3 W/m2 at 1800 MHz; and 7 W/m2 at 2100 MHz. In addition to this more stringent RF exposure limit for areas within 300 meters of children’s school/care areas and hospitals, Greece also prohibits cell towers on schools, day cares, and hospitals.
The Greek Atomic Energy Commission (EEAE) (Law 4635/2019, Article 35, paragraph 4) annually audits at least 20% of urban area base stations for compliance. Supplementary audits are carried out following requests by the national telecom regulator EETT or others.
The country maintains the National Observatory of Electromagnetic Fields, an interactive web portal linked to a network of over 500 fixed measurement stations throughout Greece that continuously monitor the EMF levels from all kinds of antenna stations in the frequency range 100 kHz – 7 GHz. The Observatory’s online map allows the public to easily access average and peak electric field strength measurements for any of the sensor locations.
Sources:
The National Observatory of Electromagnetic Fields of Greece https://paratiritirioemf.eeae.gr/en/
Rianne Stam, National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, the Netherlands
Hellenic Republic. (2000, September 6). Measures to protect the public from operation of antennas installed on land [Presidential Decree/Ministerial Decision]. Government Gazette of the Hellenic Republic, Series B, No. 1105, pp. 15829–15838. https://www.eett.gr/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/FEK1105B2000.pdf
Canada
Authority: Health Canada
Exposure Limit on Graph: 4.4 W/m² for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Toronto, Canada has a “Prudent Avoidance Policy” which recommends keeping RF exposures at least 100 times below Health Canada’s guidelines.
Sources: Safety Code 6 Health Canada. (2019, August 13). Limits of human exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic energy in the frequency range from 3 kHz to 300 GHz (Safety Code 6). Consumer and Clinical Radiation Protection Bureau, Environmental and Radiation Health Sciences Directorate, Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch. https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/health-risks-safety/limits-human-exposure-radiofrequency-electromagnetic-energy-range-3-300.html
The 4.4 W/m² limit for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density is detailed at Ramirez-Vazquez R, Escobar I, Vandenbosch GAE, Arribas E. Personal exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields: A comparative analysis of international, national, and regional guidelines. Environ Res. 2024 Apr 1;246:118124. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118124
Country: Croatia
Authority: Ministry of Health
Exposure Limit on Graph: 1.4 W/m² for 1800 W/m2 equivalent plane wave density.
The Ministry of Health is responsible for implementing measures for protection from non-ionizing radiation in accordance with the Act on Protection from Non-Ionizing Radiation (“Official Gazette”, No. 91/10) and the Regulation on Protection from Electromagnetic Fields (“Official Gazette”, No. 146/14 and 31/19). The owner of the source of electromagnetic fields is obliged, every two years, to arrange for a new measurement of electromagnetic field levels and to submit the results to the Ministry of Health
Source:
HAKOM (Croatian Regulatory Authority for Network Industries)
https://www.hakom.hr/hr/regulativa/386
Comparison of international policies on electromagnetic fields (power frequency and radiofrequency fields by Stam. National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, the Netherlands (2018).
World Health Organization RF Limits (2017)
India
Authority: Department of Telecommunications
Exposure Limit on Graph: 5 for 5G facilities and .9 W/m² for 4G 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
In 2012, India had significantly strengthened its norms to 1/10 of ICNIRP limits after its review of exposure impacts. A report from an Inter-Ministerial Committee set up by the India Ministry of Environment and Forests which reviewed the research on impacts to birds, bees, plants, humans, and other wildlife concluded that while there were significant research gaps, the “vast majority of published literature indicate deleterious effects of EMFs in various species.”
In 2024, the Indian government relaxed its norms for 5G networks, increasing the power density limit for 5G base stations from 1 watt per square meter to 5 watts. So the value on this graph shows both 4G and 5G facilities.
Sources:
Government of India, Ministry of Communications. (2012, August 31). Stringent mobile radiation standards come into force from tomorrow [Press release]. Press Information Bureau. Retrieved from https://www.pib.gov.in/newsite/PrintRelease.aspx?relid=87152
Rathee, K. (2025, January 2). In relief to telcos, 5G radiation rules eased. The Economic Times. Retrieved from https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/telecom/telecom-news/in-relief-to-telcos-5g-radiation-rules-eased/articleshow/116892570.cms
Israel
Authority: Ministry of Environmental Protection
Exposure Limit on Graph: .9 W/m² for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Israel has two limits: 30% of ICNIRP limits for areas where the exposure is not continuous and prolonged, and 10% of ICNIRP limits for areas where the exposure is continuous and prolonged (4 hours a day for five days a week) such as residential buildings, offices, and educational institutions.
The Ministry of Environmental Protection operates a RF radiation monitoring system. The system consists of 17 permanent monitoring stations deployed throughout the country near cellular broadcasting stations, radio, and television broadcasting stations. Some were also deployed in areas far away from broadcasting facilities.
Sources: Ministry of Environmental Protection, Israel. (n.d.). Non-ionizing radiation. Retrieved August 10, 2025, from https://www.gov.il/en/pages/non_ionizing_radiation
Slovenia
Exposure Limit on Graph: .9 W/m² for 1800 W/m2 equivalent plane wave density.
Slovenia has a limit for new or modified installations in sensitive areas (like homes, schools, kindergartens, hospitals, playgrounds, public buildings, and parks) set at 1/10 of ICNIRP’s recommended limits.
Source:
INIS FORUM EMS post titled “Stanje v Sloveniji”, published on 12 September 2023, includes the RF exposure limits table https://forum-ems.si/2023/09/12/stanje-v-sloveniji/
Italy
Exposure Limit on Graph: .6 W/m² for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Italy’s limits presented in this graph apply to places of “sensitive use” such as apartment buildings, schools, hospitals, permanent workplaces, children’s playgrounds, and places where people stay for hours. Italy recently loosened its strict limits, while remaining far more stringent than FCC and ICNIRP. In 2024, Italy increased the value, which was 6 V/m before the deployment of 5G, to 15 V/m. Additionally, this is based on a 24-hour average, which thus allows significantly higher levels during the busiest hours of the day.
Sources:
Italy, LEGISLATIVE DECREE 24 March 2024, n. 48
Brussels, Belgium
Note: Belgium is divided into 3 Regions (Brussels, Wallonia and Flanders). Each has their own authority regarding RF limits for their region.
Brussels RF Limits
- 1800 MHz Inside: 0.449 W/m2 same as 13.0 V/m
- 1800 MHz Outside: 1.127 W/m2 same as 20.6 V/m
- 900 MHz, Inside 0.2243 W/m2 same as 9.19 V/m
- 900 MHz outside 0.5635 W/m2 same as 14.57 V/m
Source
Leefmilieu Brussel. (2024, December 4). Wat zijn de wettelijke normen voor blootstelling aan elektromagnetische golven? [What are the legal standards for exposure to electromagnetic waves?”]
The limits were confirmed to Theodora Scarato in an email exchange with Bruxelles Environnement permit-emf@environnement.brussels dated September 1, 2025
China
Authority: Ministry of Ecology and Environment leads the creation of environmental health standards and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology ensures that telecom networks and operators comply with MEE’s exposure limits.
Exposure Limit on Graph: 0.4 W/m² for 1800 W/m2 equivalent plane wave density.
China has RF power density limits lower than ICNIRP and FCC limits. They are considered science-based as there is a strong research program in the country, and these more stringent restrictions apply to sensitive areas, such as schools, hospitals, or rooms in buildings that are regularly occupied by persons for prolonged periods. The standard also encourages facility and equipment owners to take effective measures to reduce public exposure.
Sources:
Human radio frequency exposure limits: An update of reference levels in Europe, USA, Canada, China, Japan and Korea by Madjar. International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility (2016).
Chiang, H. (2025). Rationale for setting EMF exposure standards (General public exposure limits to RF radiation in China). https://ehsciences.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Rationale-for-Setting-EMF-Exposure-Standards-China-.pdf
Russia
Authority: Federal Service for Surveillance on Consumer Rights Protection and Human Wellbeing
Exposure Limit on Graph: .1 W/m² for 1800 W/m2 equivalent plane wave density.
In Russia there is a state federal sanitary service (Rospotrebnadzor), which has branches to monitor compliance with electromagnetic field limits throughout the country. General conditions for protection of the population are set in a 1999 framework law. Limits apply to the total RF field from all sources in the environment, averaged over any 24-hour period. Limits for specific frequency ranges are set in subsequent ‘Hygienic-epidemiological requirements’.
The Russian National Committee on Non-ionizing Radiation Protection was established under the Russian Federation in 1997 and has extensive scientific publications. It serves as an national advisory body on issues related to non-ionizing radiation (NIR), including radiofrequency (RF), microwave, extremely low frequency (ELF), laser, and ultraviolet radiation. In 2008 it announced in “Children and Mobile Phones: The Health of the Following Generations is in Danger” that “for the first time in history, we face a situation when most children and teenagers in the world are continuously exposed to the potentially adverse influence of EMFs from mobile phones.” In 2019, the Russian National Committee on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection called for hazard warning signs on cell phones and other wireless devices.
Sources:
Electromagnetic radiation safety: Russian national and international regulatory frameworks for radiofrequency electromagnetic fields by Grigoriev et al. Public Health and Life Environment (2020).
Rianne Stam, National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, the Netherlands
Repacholi M, Grigoriev Y, Buschmann J, Pioli C. Scientific basis for the Soviet and Russian radiofrequency standards for the general public. Bioelectromagnetics. 2012 Dec;33(8):623-33. doi: 10.1002/bem.21742. Epub 2012 Jul 2. PMID: 22753071.
SanPiN 2.1.8/2.2.4.1190-03 “Electromagnetic fields (EMF) of radio frequencies (300 MHz–300 GHz)” (Russian Federation), § 3.3 — specifies the maximum permissible power density (ППЭ) for public exposure as 10 µW/cm² (i.e. 0.1 W/m²). Ekosf.ru hosts the text at https://ekosf.ru/normativnye-dokumenty/em-polya/sanpin-2-1-8-2-2-4-1190-03/
http://www.tesla.ru/news1: The unified platform of the Russian National Committee on Non‑Ionizing Radiation Protection (RNCNIRP), the Russian Academy of Sciences’ Radiobiology Scientific Council, and the Scientific Radiobiological Society of the Russian Academy of Sciences
http://emf-net.ru/: Russian National Committee on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection.
Bulgaria
Authority: Ministry of Health
Exposure Limit on Graph: .1 W/m² for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Source:
Ordinance No 9, issued 14 March 1991 by the Ministry of Health
Promulgated in the Official Gazette No. 35 of 3 May 1991 , amended in the Official Gazette No. 38 of 14 May 1991 , amended in the Official Gazette No. 8 of 22 January 2002. https://lex.bg/laws/ldoc/-551794688
Switzerland
Authority: Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN)
Exposure Limit on Graph: .1 W/m² for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Since 2000, Switzerland has enforced the Non-Ionizing Radiation Ordinance (NISV) under the Environmental Protection Act, which enforces stricter precautionary limits for “sensitive areas” like homes, schools, hospitals, and offices. The Swiss Federal Council refused to loosen their strict radiation limits for 5G. Locations of transmitters can be found on this map.
Sources:
Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN). (2025, April 3). Electrosmog: In brief. Retrieved from https://www.bafu.admin.ch/bafu/en/home/topics/electrosmog/in-brief.html
Comparison of international policies on electromagnetic fields (power frequency and radiofrequency fields by Stam. National Institute for Public Health and the Environment, the Netherlands (2018).
Chile
Authority: The Telecommunication Subsecretariat (SUBTEL) under Chile’s Ministry of Transport and Telecommunications.
Exposure Limit on Graph: .058 W/m² for 1800 MHz equivalent plane wave density.
Chile has a general limit of 0.1 W/m² for 1800 W/m2 applying to “any publicly accessible location without physical barriers”and a more stringent limit of .058 W/m² for 1800 W/m2 for sensitive areas like hospitals, elderly care homes, daycare centers, schools. However if 5G is deployed below 2.7 GHz (e.g., n3 at 1800 MHz), the cap is at the general limit as stated in the decree.
On June 11, 2012, Law No. 20.599 (known as the “Antenna Law”) passed, regulating the installation of telecommunications antennas and their towers. It prohibits the installation of cellular sites near “public or private schools, nurseries, kindergartens, hospitals, clinics, urban premises with high voltage towers, nursing homes, or other sensitive areas of protections so defined.”
The Minster stated, “for frequency bands between 9 kHz – 2700 MHz (technologies from 1G to 4G), the limit in general areas is 10 μW/cm² and 5.8 μW/cm² for sensitive/protected areas. For frequency bands between 2700 MHz – 300 GHz (5G technology), the limit is 400 μW/cm² for general access areas and 100 μW/cm² for sensitive areas. Additionally, if fifth-generation or higher technologies are located below 2700 MHz, their limit will be 100 μW/cm².”
The Regional Secretary of the Environment of the Republic of Chile, Sonia Reyes , stated that ” the new standards established by this regulation are among the most demanding in the world, which will allow for high-quality connectivity services, with no impact on current services. By considering electromagnetic radiation emissions as a potential pollutant, as a State we are ensuring the health and quality of life of the population and also the protection of nature.”
Source:
Ley Chile — Decreto Supremo Nº 5”, dated 11 January 2024, as published on the Biblioteca del Congreso Nacional (BCN) website
https://www.bcn.cl/leychile/navegar?idNorma=1210845&idVersion=2025-07-06
Ministerio del Medio Ambiente (Chile). (2025, February 6). Publican norma de emisión radiación electromagnética de servicios de telecomunicaciones. Aire Región Metropolitana. https://airerm.mma.gob.cl/publican-norma-de-emision-radiacion-electromagnetica-de-servicios-de-telecomunicaciones/
Law 20599 – REGULATES THE INSTALLATION OF BROADCASTING AND TRANSMITTING ANTENNAS FOR TELECOMMUNICATIONS SERVICES
https://vlex.cl/vid/antenas-emisoras-transmisoras-servicios-379211182
U.S. Lacks Scientific Oversight
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) set human exposure limits in 1996. They have remained unchanged since that date, despite the ever-growing body of scientific studies reporting harmful health-related effects at far lower exposure levels.
The Federal Communication Commission’s wireless radiofrequency (RF) radiation limits are used to assess RF levels indoors (like classrooms and homes) and outdoors (such as playgrounds and sports fields) and serve as the compliance limit for cell tower emissions.
Many international governments enforce stricter limits, especially in children’s areas. Italy and Switzerland take a precautionary approach, while China and Russia maintain active RF research programs.
However, the U.S. has no federal agency tasked with protecting public or environmental health which is conducting ongoing, robust scientific reviews of the long-term effects of cell tower radiation, despite a federal court order that they must do so issued in EHT et al. v the FCC.
Yes: There is scientific research on people living near cell towers that has linked exposure to health effects.
Click here to read dozens of studies.
- Peer Reviewed Scientific Research on Cell Towers and Health Effects
Scientific studies link cell towers to health harm
A review by Balmori 2022 examined existing research on people living near cell towers (known as mobile phone base stations internatonally) and found the majority of studies reported impacts, primarily radiofrequency sickness, cancer, and altered biochemical markers.
“Overall results of this review show three types of effects by base station antennas on the health of people: radiofrequency sickness (RS), cancer (C) and changes in biochemical parameters (CBP). Considering all the studies reviewed globally (n = 38), 73.6% (28/38) showed effects: 73.9% (17/23) for radiofrequency sickness, 76.9% (10/13) for cancer and 75.0% (6/8) for changes in biochemical parameters.”
In July 2021, the European Parliament released a commissioned report titled “Health Impact of 5G,” which concluded that widely used RF radiation frequencies (450–6000 MHz) are likely carcinogenic to humans and may harm male fertility and early development stages, such as embryos and newborns.
In 2011, RF radiation was classified as a Group 2B “possible carcinogen” by the World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer (WHO/IARC). Since then, peer-reviewed studies on both people and animals have reported increased cancer risks. The 2018 large scale animal study published in Environmental Research by Falcioni et al. found elevated cancer rates in rats exposed to RF radiation at levels permitted for cell tower emissions.
Scientists involved in the original IARC evaluation have since stated that, based on current evidence, RF radiation would likely be reclassified as a probable or even proven human carcinogen if reassessed today.
Peer-reviewed Published Research on Cell Towers and Health
Here are examples of studies in numerous countries focused on cell towers and wireless infrastructure that indicate safety is not assured:
- India: (Sailo 2025) found that residents living within 50 meters of cell towers reported significantly more adverse health symptoms than those living farther away, with symptoms that included mood, cognitive, and inflammatory issues- all at cell tower radiation exposure levels well below the current FCC safety limits.
- Germany: Gulati et al. (2024) found significantly higher rates of chromosomal aberrations—key indicators of genetic damage—in residents living near towers, supporting a biologically plausible link to increased cancer risk.
- Sweden: Hardell and Nilsson (2024) summarized several case reports on microwave syndrome symptoms in people exposed to 5G antennas.
- Brazil: Rodrigues (2021) showed higher cancer mortality, especially lung and breast, near towers.
- Spain: López (2021) linked higher RF to increased headaches, dizziness and decreased sleep.
- Italy: Brizzi and Marinelli (2019) followed a community exposed to radar from 1970 until 1998 in a community iand found increased cancer and heart disease in the exposed residents.
- Saudi Arabia: Meo (2018) linked exposure to delayed motor skills and attention deficits in teens.
- India: Zothansiama (2017) found blood changes predictive of cancer.
- India: Pachuau and Pachuaua (2016) found a strong correlation between higher tower radiation levels and health complaints with significant symptoms appearing above 2.145 mW/m².
- India: Singh et al (2016) found significantly more reported health issues—including sleep disturbances, headaches and concentration difficulties as well as measured reduced salivary secretion – in people living closer to antennas.
- Saudi Arabia: Meo (2015) reported an association between higher exposures and higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
- India: Gandhi et al. (2014), a case-control study, found significantly elevated DNA damage in residents living within 300 m of a mobile phone base station, especially among women, with power density and proximity identified as key predictors.
- Spain: Gomez-Perretta et al (2013) re-analysed the data from Navarro et al (2003) and found symptoms like fatigue, irritability, sleep disturbances, and poor concentration were linked to cellular base station exposure, independent of demographics, other EMF sources, or radiation-related anxiety.
- Taiwan: Li et al. (2012) found children living in areas with higher-than-median RF exposure had a significantly increased risk for all neoplasms (abnormal growths), benign and malignant.
- Egypt: Eskander et al. (2012) found long-term cell tower exposure over 6 years was linked to impacts to the endocrine system, including decreased ACTH, cortisol, and thyroid hormones, as well as significant drops in prolactin in females and testosterone in males.
- Brazil: Dode (2011) Cancer mortality was elevated within 500 meters of towers.
- Australia: Khurana (2011) found 8 of 10 reviewed studies showed adverse symptoms within 500m of cell towers and wireless infrastructure.
- Germany: Buchner (2011) found significant hormonal disruptions post-installation.
- Ukraine: Yakymenko (2011) reviewed dozens of studies and reported increased cancer.
- USA: Levitt & Lai (2010) reviewed 100 studies on cell infrastructure and found about 80% showed biological effects.
- Germany: Eger and Neppe (2009) found a statistically significant increase in cancer incidence among residents within a 400-meter radius of a mobile phone base station five years after it became operational.
- Egypt: Abdel-Rassoul et al. (2007) found significantly higher rates of neuropsychiatric symptoms (e.g., headaches, memory changes, sleep disturbances) and reduced attention and memory performance linked to cell phone base station antennas.
- Israel: Wolf and Wolf (2004) reported increased incidence of cancer associated with living in proximity to a cell phone transmitter station.
- Poland: Bortkiewicz et al., (2004) described increased reports of sleep disturbances, headaches, depression, and circulatory issues among people living near cell towers, with symptoms correlating to proximity and exposure level.
- Germany: Eger et al. (2004) found people living within 400 meters of a cellular transmitter had a significantly higher rate of newly diagnosed cancers and developed cancer on average 8 years earlier than those living farther away.
- France: Santini et al. (2003) surveyed 530 residents and found significantly higher rates of symptoms like nausea, sleep disturbances, and headaches within 300 m of cell towers.
- Spain: Navarro et al (2003) found a significant correlation between reported severity of “microwave sickness” health symptoms and the measured power density of RF radiation from a nearby cellular base station.
- Italy:Michelozzi et al., (1998) found significantly increased leukemia mortality, particularly in men, among residents living within 3.5 km of a high-power radio transmitter in Rome, with risk decreasing with distance.
- Latvia: Kolodynski and Kolodynska (1996) examined 609 schoolchildren and found that children residing in areas directly exposed to radar emissions exhibited statistically significant impairments in motor function, memory, attention, and reaction times.
Want to read more science? Check out our website page with published science here.
U.S. Policy on Cell Towers Near Schools
While numerous countries ban cell towers at schools, the U.S. lacks any federal laws to minimize exposure in classrooms. Some state and local communities have taken steps to safeguard children by restricting towers on school grounds or enacting ordinances to ensure a minimum setback that distances towers away from schools and homes.*
U.S. School Districts that Ban New Cell Towers
- Los Angeles CA
- Palo Alto CA
- Temecula Valley CA
- West Linn-Wilsonville OR
- Portland OR, Loudoun County VA.
Communities with Cell Tower Setback Policies:
- Encinitas, CA: 500 feet from schools, homes, and daycares
- Williamson County, TN: 1,500 ft from schools
- Copake, NY: 1,500 ft from homes/schools
- Sallisaw, OK: 1,500 ft from homes
- Walnut Creek, CA: 1,500 ft from schools
- Calabasas, CA: 1,000 ft from homes/schools
- Scarsdale, NY: 500 ft from homes/schools
- San Diego County, CA: 300 ft from schools
- Bedford, NH: 750 ft from residential property
- Bar Harbor, ME: 1,500 ft from schools
- Shelburne, MA: 3,000 ft from schools, 1,500 ft from homes
- Davis, CA: 500 ft from residential zone and schools
- Westlake Village, CA: 500 feet of homes
- Randolph, MA: 500 ft from homes
- Petaluma, CA: no “small cell” antennas within 500 ft of homes
- Suisin City, CA: no “small cell” antennas within 500 ft of homes
- Contra Costa County, CA: no new high-visibility facilities or towers within 300 ft of residential zones
- Woodstock, NY: 300 ft from any residential structure unless the small cell is co-located on an existing facility
- Ithaca NY: 250 ft from homes, schools, daycares
- Arcata City, CA: 1000 ft from homes
New Hampshire: State Commission Report on 5G Health and Environment recommends a 1,500 foot setback for cell towers and 4G/5G antennas.
International Policies to Prohibit Cell Towers Near Schools
- Russia: Antennas for cell towers and base stations are no longer permitted near schools, with a national plan in place to relocate existing sites away from schools.
- Greece: Towers are banned on school grounds. Stricter RF limits apply within a 300-meter radius around kindergartens, schools, hospitals, and elderly care facilities.
- France: Radiation levels must be minimized for towers or wireless facilities within 100 meters of schools, daycare centers, or healthcare establishments.
- Bangladesh: Cell towers are prohibited on residential properties, schools, colleges, playing fields, densely populated areas, and heritage sites.
- Israel: Minimum setback of 100 meters for cell towers near schools and homes.
- Chile: Cell antennas are not allowed in “sensitive areas” such as kindergartens, hospitals, and nursing homes.
- Queensland, Australia: New cell towers are prohibited on school property, with a 200 meter setback and emissions capped at no more than 1% of federal guidelines.
- New Zealand: Cell towers are prohibited on school property and a 50 meter setback from schools is required.
- Toronto, Canada: A “Prudent Avoidance Policy” recommends keeping RF exposures at least 100 times below Health Canada’s guidelines.
- India: Cell towers are prohibited or removed near schools, colleges, orphanages and old age homes in Mumbai, Zilla Parishad, Rajasthan & Karnataka.
- Turkey: Cell antennas must be distanced from schools and playgrounds and not placed on the same floors as preschools or primary schools in multi-story buildings. RF levels are continuously monitored near schools and hospitals.
- Benin: A 2021 interministerial order requires base station sites (cell towers or 4G/5G network antennas) to be located at least 100 metres away from “sensitive’ locations such as daycares, schools, orphanages, hospitals, and public parks. The Administration applies ICNIRP reference levels, but if a tower is in the buffer zone it must be compliant with an additional reduction factor to 25% of the limit. A certificate of electromagnetic compliance is required before operation, renewed every 2 years.
- Egypt: In 2022, Egypt established a national committee, consisting of the National Telecom Regulatory Authority, the Environmental Affairs Agency, the Ministry of Health and Population, and the National Telecommunication Institute, which updated guidelines with the condition that a single antenna does not exceed 5% of the limit. The base of a tower must be at least 12 meters from the fence of any school and not at schools. Macro site antennas cannot be placed on hospital roofs.
What exposure level is safe?
The only way to ensure long-term safety is to base exposure limits on independent, ongoing scientific research. Most policies, whether in the U.S. or abroad, remain anchored in the decades-old assumptions that short-term heating effects are the only harm caused by RF radiation. Yet modern studies consistently report biological impacts at non-heating exposure levels and after long-term exposure. Until governments systematically integrate new evidence into updated health-protective standards, the public, especially children, remains inadequately safeguarded.
Even countries with stricter environmental limits are not necessarily ensuring safety, because a growing body of research reports biological effects at very, very low intensities. This is why mitigating exposure as much as possible by using wired tech and wired networks instead of wireless is the best path forward.
A 2022 published review of studies on people living near cell towers found the majority of studies reported impacts, primarily radiofrequency sickness, cancer, and altered biochemical markers. Read more science here.
