Cell phones are ubiquitous in our children’s lives. They, along with the cell towers they connect to, emit a type of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation called radiofrequency or RF radiation. Scientists point to several cell phone radiation risks for children, as scientific research reports impacts to memory, sleep, neurodevelopment, hormones, and numerous other health risks.
A published analysis of the U.S. National Toxicology Program experimental study that found clear evidence of cancer, concluded that U.S. FCC limits should be strengthened by at least 200 to 400 times to better protect children.
Why Children Are More Vulnerable
Children are not simply “small adults.” Their anatomy, physiology, and rapid development make them uniquely vulnerable to radiofrequency (RF) radiation from cell phones and wireless devices.
Here is why.
Smaller Heads and Thinner Skulls
Children have smaller heads and thinner skulls than adults, which allows RF radiation to penetrate deeper into their brain and body. Government exposure limits were based on testing using a large adult male head model, not a child’s. Scientific modeling has found RF absorption rates in children are higher than in adults, 2-fold greater in the cerebellum, 2 to 5-fold in the eyes, 10-fold greater in the skull, and 30-fold greater in the hippocampus.
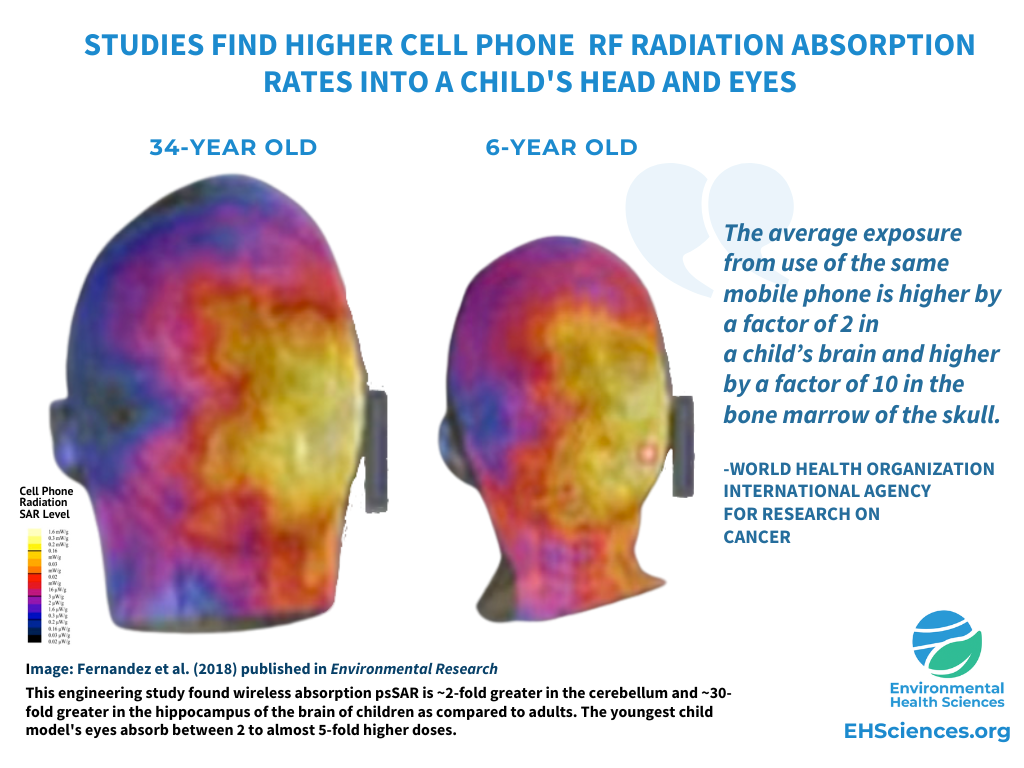
Rapidly Developing Brains
During childhood, the brain undergoes rapid growth and development. This period of heightened neuroplasticity makes the brain more sensitive to environmental stressors. Experimental studies have found that even low-level microwave exposure can damage brain cells, alter neural signaling, and increase cell death in developing brains. Disruption during early development may result in long-term neurological and cognitive effects.
Higher Water Content in Brain Tissue
Children’s brains and bodies contain a higher proportion of water than adults. Because electromagnetic energy travels more efficiently through water-rich tissues, RF radiation can penetrate more intensely into children.
More Active Stem Cells
Children have a higher number of active stem cells, which are responsible for growth and development. Research indicates that stem cells may be more sensitive to low-level RF radiation, raising concern that critical developmental processes could be affected.
Smaller Bodies and Closer Device Use
Children’s shorter arms and smaller bodies mean they hold phones, tablets, and laptops closer to their heads and bodies. When devices are used against the body, especially tablets with multiple antennas, a greater proportion of a child’s body is exposed compared to an adult using the same device.
Multiple Phones and Wi-Fi Laptops in Classrooms
Children have numerous overlapping exposures all at once. An engineering study simulating a classroom of children found RF radiation exposure to a child’s head and back increased up to 40-fold when surrounded by other children with Wi-Fi emitting laptops, due to the cumulative emissions from all the nearby Wi-Fi laptops. Toddlers are given tablets in daycares. Parents are unaware of this exposure.
Cell Towers Are Increasing Children’s Daily Exposure
When antennas are installed near schools, RF radiation levels increase across school grounds and surrounding areas where children spend much of their day.
- An Australian study found that kindergarten students attending schools near cell towers experienced more than three times higher total RF exposure than children at schools without nearby towers.
- Research also shows that cumulative exposure from nearby cell towers can exceed the RF radiation young children receive from typical cell phone use. A 2023 study published in Environmental Research by Lee and Choi reported that continuous 24-hour downlink signals from cell towers resulted in more than a ten-fold higher cumulative daily brain energy absorption in children compared to exposure from mobile phone use alone.
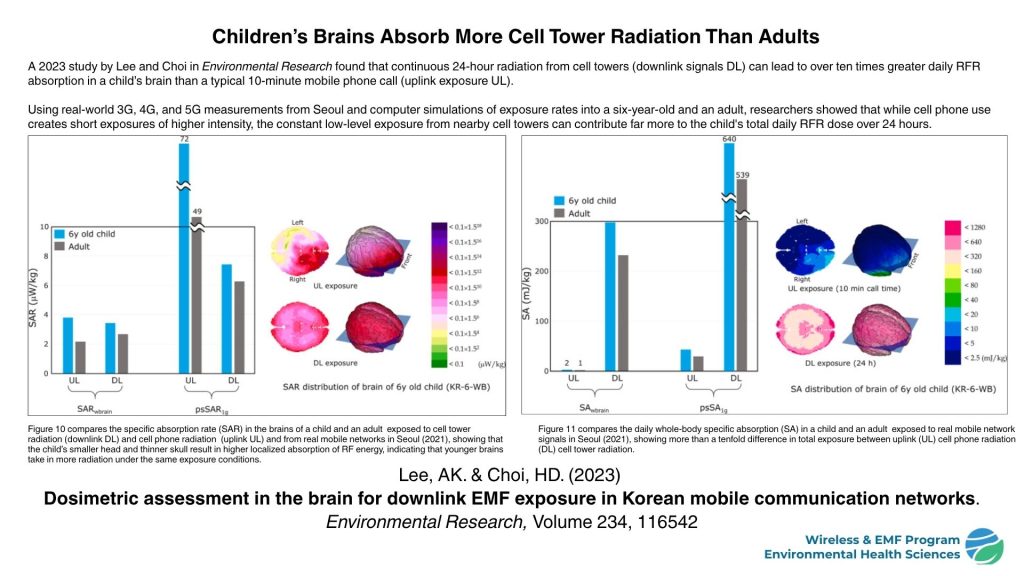
A Lifetime of Exposure, Starting During Pregnancy
Exposure to RF radiation during pregnancy warrants special attention because fetal development is highly sensitive to environmental stressors.Yale scientists exposed pregnant mice to cell phone RF radiation emitted by cell phones and reported prenatally exposed mice had memory deficits, increased hyperactivity, and structural brain changes. Further studies on mice have found demyelination and hyperactivity. Human research studies have repeatedly linked prenatal cell phone radiation exposure to emotional and behavioral problems in children.
What the Science Shows
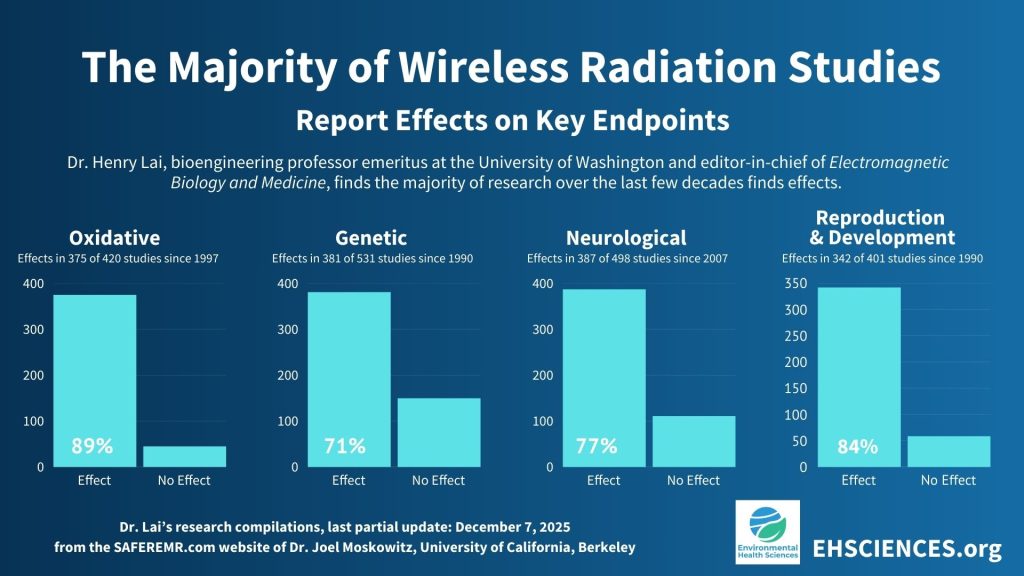
A growing body of peer‑reviewed scientific research documents biological effects associated with RF radiation exposure at levels below current U.S. limits.
Here are some research studies to know.
Sleep: An experimental study found that individuals with specific gene variants who are exposed to 5G frequencies experienced changes in their brain wave activity during sleep. A study examining the impact of baby monitor RF on sleep quality found exposed adults experienced significantly reduced sleep quality and changes in EEG readings of brain activity during Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep.
Colorectal cancer: A Kaiser Permanente research team is investigating cell phone radiation and colorectal cancer. Studies are ongoing, however they presented preliminary findings at the International Society of Environmental Epidemiology Conference in a poster entitled, “Is Cellphone Carrying Below the Waist (Exposure to Non-Ionizing Radiation) Contributing to the Rapid Rise in Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer?“ Their analysis reports that people who carried a phone on the left side for more than 30,000 hours were 12 times more likely to develop a tumor on that side of the colon.
Brain and Thyroid Cancer: The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), a part of the World Health Organization (WHO), classified cell phone radiation as possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B) in 2011 based on evidence linking heavy cell phone use to cancer. Today, numerous scientists state the scientific evidence has increased to the point that RF radiation would be classified by IARC as a “probable” or “proven” human carcinogen if re-evaluated based on current research. Yale School of Public Health has linked cell phone use to thyroid cancer. Published case reports and case-control studies have documented that women who carry cellphones in the bra have elevated breast cancer risk.
Genetic Impacts: A review of over 500 studies on genetic impacts published in Frontiers in Public Health found that a substantial body of scientific research has reported genetic damage from wireless radiation exposure in both humans and animals.
Brain Activity: The brain is particularly sensitive to wireless radiation exposure. A National Institutes of Health study found that cell phone use altered brain activity, changing glucose metabolism in regions closest to the phone’s antenna.
Memory Damage: In a European study of adolescents, researchers directly estimated the amount of RF radiation absorbed by the brain and found that higher cumulative brain dose from cell phone use over just one year was associated with damaged memory. The effect was specific to figural memory and to the brain regions on the side of the head most exposed during phone calls, supporting a dose–response relationship rather than an effect of screen time alone.
Developmental Delays: A recent study that directly measured RF radiation levels in the home environment found that children with higher exposure scored significantly lower on gross and fine motor skills and showed poorer performance in problem-solving and personal-social development compared to children with lower exposure.
Animal studies consistently show that wireless radiation exposure can impact the blood brain barrier, impact brain development and damage brain cells, particularly in brain regions critical for learning and cognition, including the hippocampus, with several researchers concluding that such structural damage may lead to behavioral changes and long-term neurological effect.
Impacts to the Endocrine System
Studies have reported that the endocrine system, which regulates hormones, can be disrupted by wireless and EMFs. Research has found impacts on thyroid gland activity, adrenal function, and corticosterone levels, a hormone central to the body’s stress response. This is important because hormones are central to brain development, metabolism, reproduction, and the body’s stress response. Experimental animal studies have found that prenatal exposure led to a decrease in rats’ estrogen and progesterone hormone levels, impacted the size of the rats’ ovaries, and reduced the number of developing follicles.
- Research on Wireless, EMF and the Endocrine System
Narayanan et al. (2025) in Behavioural Brain Research found radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation exposure altered contextual fear memory, hippocampal structure, and adrenal gland microarchitecture in male rats.
Kim et al. (2024) in International Journal of Molecular Sciences showed adolescent male mice exposed to 4G LTE altered T3 levels in the blood and Dio2 and Dio3 gene expression in the hypothalamus, “suggesting potential HPT axis disruptions at the molecular level.”
Zhou et al. (2024) in Scientific Reports found longer daily use of Bluetooth headsets strongly linked to an increased risk of developing thyroid nodules.
Serin et al. (2023) in Journal of Molecular Structure found Wi-Fi radiofrequency exposure altered gene expression in rat thyroid tissues.
Zufry et al. (2023) in Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research reported that mobile phone electromagnetic radiation impacted thyroid stimulating hormones as well as a type of protein key to transporting thyroid hormones in the brain and other tissues.
Cantürk Tan et al. (2022) in Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine found that pre- and postnatal 2450 MHz radiofrequency exposure across four generations affected thymus development. They conclude that “pre-and postnatal 2450 MHz continuous wave radiofrequency radiation exposure may potentially affect the thymus of future generations.”
Perov et al. (2022) in Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine found daily exposure to 5G base station EMF disrupted the neuroendocrine system status in male rats. “The results suggest that exposure to a multifrequency EMF exposure simulating the effects of 5G systems affected functional activity of the hypothalamus—pituitary—adrenal axis and was stressful in nature.”
Alkayyali et al. (2021) in Cureus reviewed the research on non-ionizing EMF and thyroid hormones for both radiofrequency and extremely low frequency radiation and found altered thyroid hormone levels and impacts to thyroid tissue.
Rubtsova et al. (2019) in Radiatsionnaya Biologiya Radioekologiya of the Russian Academy of Sciences reported that 2.4 GHz low-intensity radiofrequency exposure impacted exploratory behavior “and may be associated with a decrease of cognitive processes and long-term memory of animals.”
Perov et al. (2019) in Bioelectromagnetics found that a very low level of 171 MHz low-intensity electromagnetic field exposure stimulated adrenal gland activity in rats. The authors conclude, It is possible that EMF exposure causes a stress response in animals, which is seen as an increased adrenal activity.”
Asl et al. (2019) in Environmental Science and Pollution Research conducted a systematic review and reported studies had found a reduction in diameter of thyroid follicles, histological changes in the thyroid gland follicles and impacts to thyroid hormones.
Perera et al. (2018) found that high-frequency EMFs (18 GHz) made PC12 neuroendocrine cell membranes more permeable, affecting molecule transport. The researchers state that the results suggest a possible use of EMFs to facilitate efficient transport of biomolecules, dyes and tracers, and genetic material across cell membrane in drug delivery and gene therapy. However, since endocrine cells release hormones into the body, changes in membrane control could disrupt how signals and hormones are released, potentially influencing communication in the nervous and endocrine systems.
Yüksel et al. (2016) in Endocrine found that long-term mobile phone and Wi-Fi exposure decreased plasma prolactin, progesterone, and estrogen while increasing uterine oxidative stress in pregnant rats and their offspring. “These results also suggest that exposure to mobile phones and Wi-Fi emitting EMR frequencies appears to affect rat endocrine functions and oxidative stress values, and indicate the need for further studies investigating the effects of such exposure in humans.”
Sangün et al. (2015) in Pediatric Endocrinology Reviews reviewed research on how electromagnetic fields could affect the endocrine system in children and adolescents. While results could be conflicting, they found studies observing detrimental effects on thyroid function, adrenal hormones, glucose homeostasis and melatonin levels.
Shahryar et al. (2009) in Bulletin of the Veterinary Institute in Pulawy found that exposure to 900 MHz electromagnetic fields from cellular phones altered T3, T4, and increased serum cortisol levels in hamsters.
Sinha (2008) in International Journal of Radiation Biology reported that chronic non-thermal exposure to 2450 MHz microwave radiation altered thyroid hormone levels and induced behavioral changes in male rats.The authors state that, “Low energy microwave irradiation may be harmful as it is sufficient to alter the levels of thyroid hormones as well as the emotional reactivity of the irradiated compared to control animals.”
Impacts to the Reproductive System:
A large body of human and animal studies consistently report that wireless radiation can impact sperm. Documented impacts include reduced sperm count, motility, and concentration; DNA damage; altered structure; and higher rates of erectile dysfunction. A literature review on the effects to male reproductive hormones concluded testosterone reduction. Reproductive impacts are not limited to males as laboratory studies on female animals link exposure to damage to ovarian follicles, disrupted cycles, and adverse effects on early embryonic development.
The European Parliament’s 2021 “Health Impact of 5G” report concluded that radiofrequency radiation (450–6000 MHz) is likely carcinogenic, clearly harms male fertility, and may adversely impact embryos and newborns.
EMFs can amplify other toxic exposures.
Children are exposed to numerous environmental pollutants, such as air pollution, pesticides, heavy metals, and chemicals, and research shows that non-ionizing EMFs can interact with these toxins to increase their harmful effects. Studies have found that exposure can intensify the biological impacts of substances like lead, pesticides, and air pollution, leading to greater inflammation, immune disruption, neurobehavioral effects, and increased toxicity than either exposure alone.
Examples of Studies on Wireless and Non-ionizing EMF Finding Synergistic Effects
Black Carbon
López-Martín et al. (2023) in Sensors reviewed the impact of EMFs and wireless on cell cultures and reported that black carbon particles and/or radiofrequency electromagnetic fields increases toxicity, raising inflammatory responses, activating apoptosis, and accelerating cell damage.This means that in polluted air, especially during thermal inversions, when dirty air gets trapped close to the ground, wireless signals might worsen the harmful health effects of air pollution by making cells more inflamed or damaged.
Sueiro Benavides et al. (2023) in Science of The Total Environment reported that combined exposure of HL-60 human promyelocytic cells to black carbon particles and 2.45 GHz radiofrequency induced oxidative stress, and enhanced cell toxicity in the promyelocytic cell line.
Sueiro Benavides et al. (2021) in Science of the Total Environment reported on an in vitro study that found black carbon particles, found in air pollution, combined with 2.45 GHz radiofrequency exposure combined induced cell damage and an inflammatory response, activating apoptosis (programmed cell death) and accelerating cell toxicity in the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line.
Lead
Choi et al. (2017) in Environmental Research reported that while no association was found between prenatal RFR exposure and child neurodevelopment impacts during the first three years of life; however, a potential combined effect of prenatal exposure to lead and mobile phone use was suggested. Among children whose mothers had high blood lead levels during pregnancy, a higher average maternal calling time was associated with an elevated risk of low Psychomotor Development Index scores up to 36 months. Similarly, greater calling time or frequency was linked to declines in the Mental Development Index.
Ansarihadipour & Bayatiani (2016) in Iranian Red Crescent Medical Journal reported that lead in the presence of EMF exacerbated the oxidative damage to plasma proteins in human blood samples.
Atrazine
Rajkovic et al. (2010) in Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology reported that peripubertal male rats exposed to both the endocrine-disrupting herbicide atrazine and power-frequency EMF showed significant degranulation of cutaneous mast cells, with combined exposures producing stronger effects.
Phthalates
Chen et al. (2021) in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety reported that combined exposure to Di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) and 50 Hz magnetic fields (MF) enhanced proliferation of human amniotic cells.
“Given that both MF and DEHP are ubiquitous environmental contaminants, the adverse effect of co-exposure at “safe levels” should not be underestimated. In this study, we detected that co-exposure to under-threshold MF and DEHP could significantly promote FL [human amniotic] cell proliferation, suggesting that certain chemical and physical environmental stimuli at “safe-level” could induce synergistic effect indeed. Considering that abnormal cell proliferation was related to the occurrence and development of some diseases, the combined effect on FL cell, a representative cell from the reproductive system, could provide clues for further research on reproductive toxicity.”
Caffeine
Panagopoulos (2020) in General Physiology and Biophysics reported that human lymphocytes exposed to RF radiation at levels well below ICNIRP limits showed chromatid-type aberrations comparable to extremely high caffeine doses, and that combined exposure (RF radiation plus caffeine) produced dramatically higher genotoxic chromosome damage.
Shift Work
Khosravipour et al. (2024) in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety reported that prolonged occupational co-exposure to extremely low-frequency EMF, noise, and rotating shift work was associated with significant alterations in thyroid hormone levels (increased TSH, altered T3 and T4).
Fructose
Tripathi et al. (2023) in Biomedical and Environmental Sciences reported that combined cell phone RF radiation exposure and high fructose intake disrupted metabolic regulators in growing rats. “Conclusion: The findings suggest that the combination of EMF exposure and fructose consumption during childhood and adolescence in Wistar rats disrupts the closely interlinked and multi-regulated crosstalk of insulin receptor signals, mitochondrial OXPHOS, and the antioxidant defense system in the hypothalamus and liver.”
Gold Nanoparticles
Jooyan et al. (2023) in Chemosphere reported that RFR increased metabolic death in chinese hamster ovary cells treated with gold nanoparticles.
Ionizing Radiation
Panagopoulos (2024) in General Physiology and Biophysics reported that cell phone radiation induced genotoxic effects and significantly amplified gamma radiation, induced chromosome damage in human cells at 136 times below ICNIRPs limit.
Soffritti et al. (2016) in International Journal of Radiation Biology reported that lifelong exposure to 50 Hz magnetic fields combined with γ-radiation promoted carcinogenesis in rats.’ These results call for a re-evaluation of the safety of non-ionizing radiation.”
Soffritti et al. (2016) in American Journal of Industrial Medicine reported synergism between 50 Hz magnetic fields and formaldehyde in producing carcinogenic effects in male rats.
Soffritti and Giuliani (2019) in Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology reported on their large scale animal studies finding that both 50 Hz magnetic fields and 1.8 GHz GSM radiofrequency radiation demonstrated carcinogenic potential.
Obajuluwa et al. (2023) in Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences reported that co-exposure to 5 GHz router radiation and computed tomography (CT) scans produced heightened neurotoxic ( impairments in spatial working memory and exploratory behavior) cytotoxic, and genotoxic effects in male rats compared to CT alone.
Khodamoradi et al. (2022) in Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports reported that combined gamma radiation and Wi-Fi exposure “can increase the number of double-strand break DNA in peripheral blood lymphocytes to exposure of gamma-ray to 72 h after technetium injection in the rat.”
Cao et al. (2009) in Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part A reported that the combination of EMF and γ-ray exposure resulted in a synergistic effect by triggering stress response, which increased reactive oxygen species.
Ethylnitrosourea (ENU)
Lerchl et al. (2015) in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications found tumors of the lungs and livers as well as lymphomas to be significantly elevated in mice prenatally exposed to ENU, a chemical that causes cancer, replicating the results of an earlier study by Tillman et al. (2010).
“Our study confirms and extends the previously published observations of tumor-promoting effects of life-long RF-EMF exposure.”
“The fact that both studies found basically the same tumor-promoting effects at levels below the accepted (and in most countries legally defined) exposure limits for humans is worrying. Although animal experiments are generally not easily transferable to the situation in humans, the findings are a very clear indication that – in principal – tumor-promoting effects of life-long RF-EMF exposure may occur at levels supposedly too low to cause thermal effects.”
“Our findings may help to understand the repeatedly reported increased incidences of brain tumors in heavy users of mobile phones.”
Tillmann et al. (2010) in International Journal of Radiation Biology reported that lifelong RF exposure enhanced lung tumour incidence and metastasis in ethylnitrosourea-pretreated mice, suggesting a cocarcinogenic potential.
Multifrequency Non-ionizing EMF
Wang et al. (2022) in Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety reported that combined 1.5 and 4.3 GHz microwave exposure impaired spatial learning and memory abilities and impacted hippocampal structure.
Zhao et al. (2022) in International Journal of Molecular Sciences reported that multi-frequency microwave exposures (1.5 and 4.3 GHz) produced immune suppressive responses.
Zhu et al. (2021) in Scientific Reports reported that 1.5 and 4.3 GHz microwave exposure impaired cognition and altered hippocampal structure in rats. Combined exposure to both frequencies caused more serious injuries.
Byun et al. (2013) in PLOS ONE reported that heavy cell phone use was associated with increased ADHD symptom risk in children, but this effect was limited to those with higher blood lead levels, suggesting a combined toxic interaction between RF exposure and lead.
5G
Kostoff et al. (2020) in Toxicology Letters reported that 5G mobile networking technology, when assessed under real-life conditions, may pose adverse health effects due to cumulative exposures and synergistic interactions with other environmental stressors.”5G mobile networking technology will affect not only the skin and eyes, but will have adverse systemic effects as well.”
Nicotine
Emre et al. (2021) in South East European Journal of Immunology reported that 900 MHz RF-EMR alone induced harmful effects in human fetal amniocytes, and the combination with nicotine further increased apoptosis and necrosis.
A note on Bluetooth
While Bluetooth radiation is much lower than that of a cell phone to the head, this does not mean it is safe. Research by Yale University scientists found that exposure to wireless radiofrequency (RF) radiation at Bluetooth frequency and low power – approximately 4,000 times lower (0.025%) than the FCC’s current allowable limit for human RF exposure interfered with neurodevelopment and increased the expression of autism-related genes in laboratory models of the fetal brain. A study published in the journal Scientific Reports found that prolonged daily use of Bluetooth headsets was “strongly linked” to an increased risk of developing thyroid nodules.
Schools and Daily Exposure
Schools are now dense wireless environments, often filled with multiple overlapping sources of RF radiation:
- Classroom Wi‑Fi networks
- Student laptops and tablets
- Cell phones carried on bodies throughout the day
- Bluetooth devices and smart boards
- Nearby cell towers or small‑cell infrastructure
Children may be exposed for six to eight hours a day during critical periods of brain development.
Global policies to reduce exposure
- Over 20 countries have recommendations to reduce cell phone radiation exposure, with several adopting laws focused on protecting children.
- Several countries have banned the sale and advertising of cell phones designed for young children, and reduce Wi-Fi exposure in schools.
- Several countries have banned cell towers on school property.
U.S. Government Limits Do Not Protect Children
The U.S. is among the countries that allow for the highest levels of cell tower RF radiation in the environment. The graph below shows the selected countries’ regulations regarding public exposure limits for 1800 W/m2 equivalent plane wave density RF radiation, applicable to schools and/or homes. Many countries have limits that apply to places of “sensitive use” such as apartment buildings, schools, hospitals, permanent workplaces, and children’s playgrounds. The U.S. has no specific safeguards for children or schools.
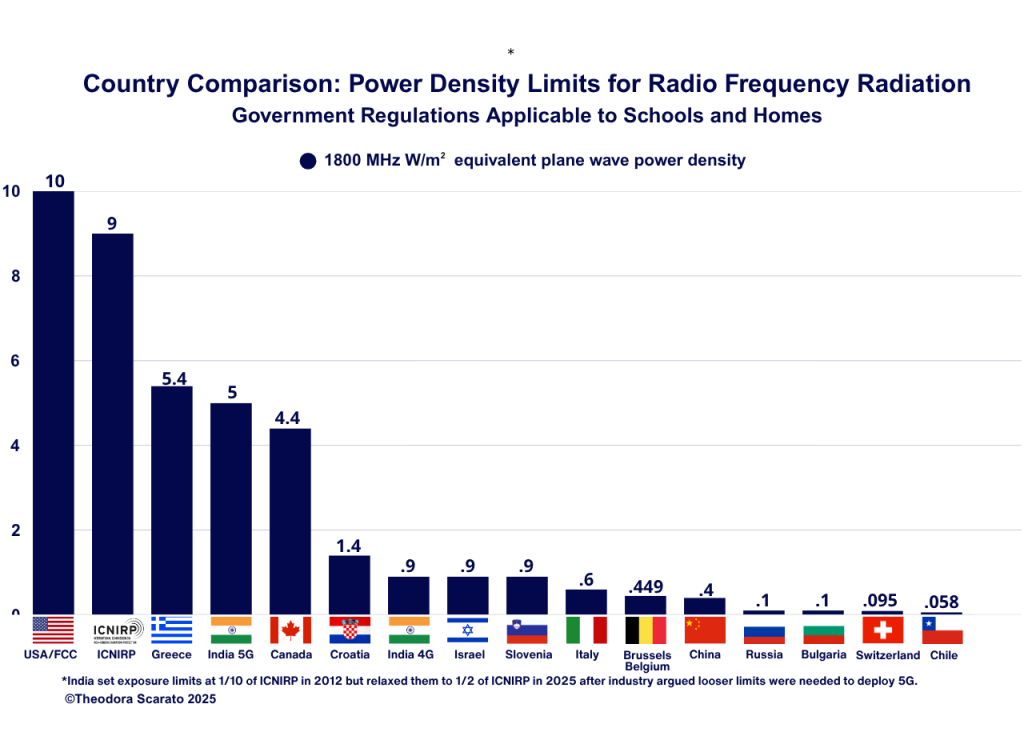
Federal Court Ruling on Children’s Vulnerability
In a landmark 2021 federal court ruling, the U.S. Court of Appeals ordered the FCC to explain how its outdated exposure limits specifically protect children.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) had submitted multiple letters urging the FCC to reassess its limits to reflect modern device use and to protect pregnant women and children, stating, “Children are disproportionately affected by environmental exposures, including cell phone radiation,” and “current FCC standards do not account for the unique vulnerability and use patterns specific to pregnant women and children. It is essential that any new standard for cell phones or other wireless devices be based on protecting the youngest and most vulnerable populations to ensure they are safeguarded throughout their lifetimes.”
Yet the FCC ignored the letters.
The FCC was also sent appeals from public health groups and hundreds of scientists who signed the EMF Scientists Appeal and European Union 5G Appeal, as well as resolutions from medical associations worldwide calling for risk reduction measures, especially for children.
However, in 2019, the FCC dismissed their appeals without explanation and stated U.S. cell phone radiation limits set in 1996 did not need to be updated.The Court found the FCC had broken the law by not addressing their requests.
The judges stated in their 2021 court order:
“The Commission’s failure to provide a reasoned or even relevant explanation of its position that RF radiation below the current limits does not cause health problems unrelated to cancer renders its explanation as to the effect of RF radiation on children arbitrary and capricious.”
— 2021 DC Circuit Decision in Environmental Health Trust et. al. v the FCC
Years later, the agency has still failed to respond to the 2021 federal court order or update its regulations.
What Needs to Change
To protect children and future generations, the U.S. must modernize its approach to wireless safety:
- Update exposure limits based on current science and real‑world use
- Require testing that reflects body‑contact and continuous exposure
- Establish national monitoring and public disclosure of RF radiation levels
- Reduce unnecessary wireless exposure in schools
- Prohibit cell towers on or adjacent to school property
- Educate families and educators about exposure reduction
Download our factsheets and resources to learn more.
